
What MADe Does
MADe is used to enable better decisions about the design and support of safety / mission critical equipment at each stage of the product lifecycle.
Reduce risk using interdependent analysis capabilities that consider the technical, operational and economic requirements of the operator and/or maintainer of the system.

Maintenance Optimization of Legacy Army Assets

Establish Life Cycle Costs For A Bid / Proposal

Design for CBM
Maintenance Optimization of Legacy MaritimeAssets
Capabilities
MADe for Airworthiness
MADe for Asset Management
MADe for Reliability
MADe for CBM
MADe for FRACAS
MADe for Safety
Who uses MADe

Executive Level

Manager level

Academic (Research)

Engineer / Analyst level
When to use MADe
MADe improves the quality of decision making at every step of a system’s lifecycle (Bid / Proposal, Acquisition, Design, and Sustainment / Asset Management).
There are compounding benefits if MADe is applied from the initial stage of a project, the advantages of MADe support a business case for implementation for stand-alone analysis (e.g. FMECA or Maintenance Optimization)
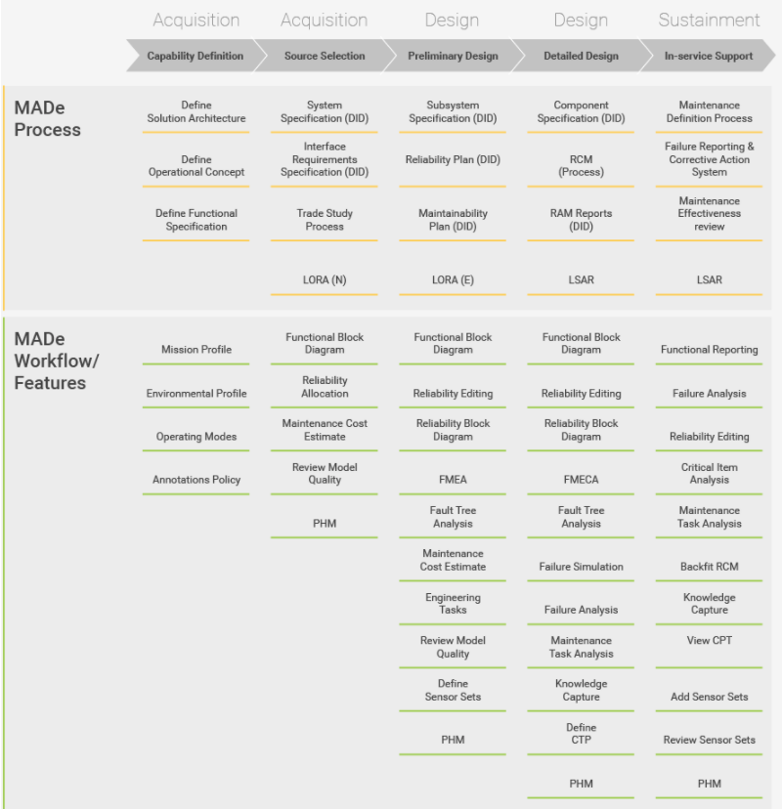
How MADe Works
MADe is a model based technology – where each block in the model is associated with key attributes / parameters including the functional description, failure information, criticality of each (cause, mechanism, fault, symptoms), etc.
MADe can be used to model the functional requirements of a platform of a design (at all stages in the design process) or for legacy equipment. As the design matures to the point where specific equipment is identified, indenture levels can be added to the model for the systems, sub-systems, assemblies, components and parts (if required for analysis).
The ability to rapidly generate or update the system model means that it is possible to introduce configuration management of the analysis process – particularly difficult to achieve with spreadsheet based tools
Why use MADe
MADe is an advanced, model-based decision support solution for complex engineering systems.

Complexity of systems and design
Systems developed by the OEMs increasingly combine electronics, hydraulics, mechanical components and sub-systems comprising thousands of ‘moving parts’. The greater the complexity of the system, the harder it is for an engineer to manually map the dependencies of failures between hierarchies and domains and therefore to identify potential risks. Complexity is a strong driver for OEMs to introduce technology such as MADe that is designed to reduce the complexity of the process for the engineer by ensuring that dependency modelling (or mapping) is achieved ‘automatically’ throughout the system rather than relying on the engineer.

Distributed design responsibility
Increasingly OEMs are devolving design responsibility to their design partners and lower tier suppliers while they focus on systems engineering and integration. However, a key issue for the OEMs is that they then use the design / failures data generated by their partners as the basis for analysing reliability and developing diagnostic capabilities. Therefore, there are strong drivers for the OEM to introduce technology that can increase standardisation into the design process in order to improve quality and analysis capabilities.

Divergence in Total Cost of Ownership
Significant variances develop in the support costs associated with complex systems, often because the costs of support are not considered appropriately during the design phase. MADe provides the potential to “Design for Support” instead of simply supporting the design based on its support of concurrent engineering practice to consider the ‘Supportability Influence’.

Performance Based Contracting (PBC)
Also referred to as Vendor Based Logistics (VBL) effectively transfers the financial risk of operating and maintaining equipment from the customer to the OEM. PBC means that OEMs are increasingly focused on technologies that can assist them to increase the reliability of their systems and therefore decrease the maintenance / logistics footprint required to support them (the major component of cost of ownership)
Advantages of MADe
MADe is an advanced, model-based decision support solution for complex engineering systems.

Operational
- Optimize system availability (Readiness)
- Minimize downtime (Mission impact)
- Ensure ‘safe as practical’ operations
- Engineering decision support for supportability analysis

Cost
- Optimize cost of ownership
- Reduce the cost of engineering analyses (accelerate productivity)
- Reduce the schedule impact of engineering analyses
- Technical decision support for economic trade studies

Process
- Design / Acquire / Operate with support considerations
- Traceability of analysis across the product lifecycle
- Knowledge capture / management across the product lifecycle
- Model-based decision support with engineering analysis
Where MADe Is Used
MADe provides modelling, analysis and decision support to identify and mitigate engineering risk based on its identified potential technical, operational and economic consequences.
MADe is a decision support solution based on engineering analysis that provides the right information and analysis to efficiently make design / project / program decisions that are technically valid and economically justified at every stage of the product lifecycle.

Aviation
Aviation companies operate with global design, supply, build and service processes; under accelerated system upgrade and enhancement timelines; in an industry moving to performance based contracting. Increasingly significant economic and reputation impacts are linked to system reliability and through-life costs.

Military
Shrinking national defence budgets, increasingly complex and integrated systems, and the push for Performance Based Contracting combine to challenge the existing design and sustainment methodologies for defence systems and equipment.

Oil and Gas
The operational, financial and environmental risks of system failure; a highly regulated industry and harsh operating conditions offer specific challenges for the systems that are used in the Oil & Gas sector.

